ROS4HRI
ROS for Human-Robot Interaction (ROS4HRI) is the standard ROS API for your robot to represent information about the human surrounding and interacting with the robot.
Overview
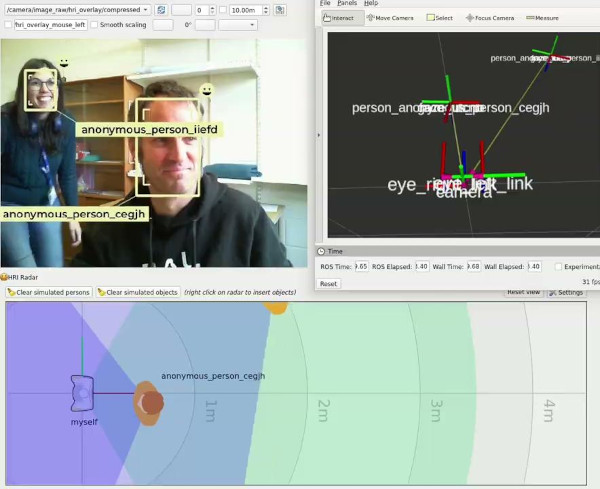
ROS4HRI (Robot Operating System for Human-Robot Interaction) is the standard ROS API for representing and managing information about humans in a robot’s environment. Officially accepted as REP-155, it provides a common language for social robots to perceive, interpret, and respond to human signals, independent of the underlying sensors or algorithms.
Objectives
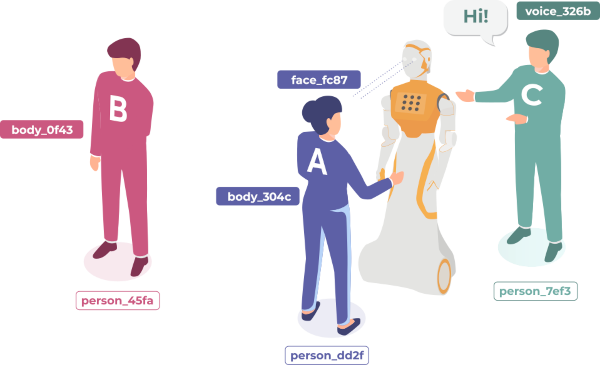
- Standardization: Establish a unified ROS API (REP-155) for human representation (faces, bodies, voices, and persistent person entities).
- Interoperability: Enable different HRI components (person trackers, face recognizers, gesture detectors) to work together seamlessly.
- Reusability: Promote the development of sensor-agnostic and algorithm-agnostic HRI software tools.
- Reproducibility: Facilitate benchmarking and comparative evaluation of HRI algorithms through standardized interfaces.
Technology
- REP-155 Specification: The core standard defining naming conventions and message structures for social robotics.
- hri_msgs: Standardized ROS messages for human-related data such as skeletal joints, 2D/3D regions of interest, and engagement levels.
- libhri: High-level C++ and Python libraries designed to simplify the aggregation and access of human-related signals for developers.
- Multimodal Integration: Support for fusing data from vision, audio, and depth sensors into persistent, unique person IDs.
- Visualization Tools: Specialized RViz plugins for real-time visualization of human skeletons, gaze, and social space.
Impact
ROS4HRI is transforming social robotics development by reducing redundant custom implementations and enabling modular HRI software stacks. It is a foundational component in numerous international research projects ranging from autism therapy (https://socialminds.iiia.csic.es/projects/emorobcare/) to human-centered industrial collaboration. By making HRI software shareable across different robot platforms, it significantly accelerates the transition from university research to real-world social impact.
Get Involved
- GitHub: Contribute to the core libraries and perception modules on our GitHub organization.
- Documentation: Explore the complete specification, tutorials, and getting started guides at ros4hri.github.io.
- Community: Join the discussion on the ROS Discourse HRI category to help shape the future of the standard.

 Project Team
Project Team